What Planting Zone is Texas?[Map, Cities, and Growing Tips]
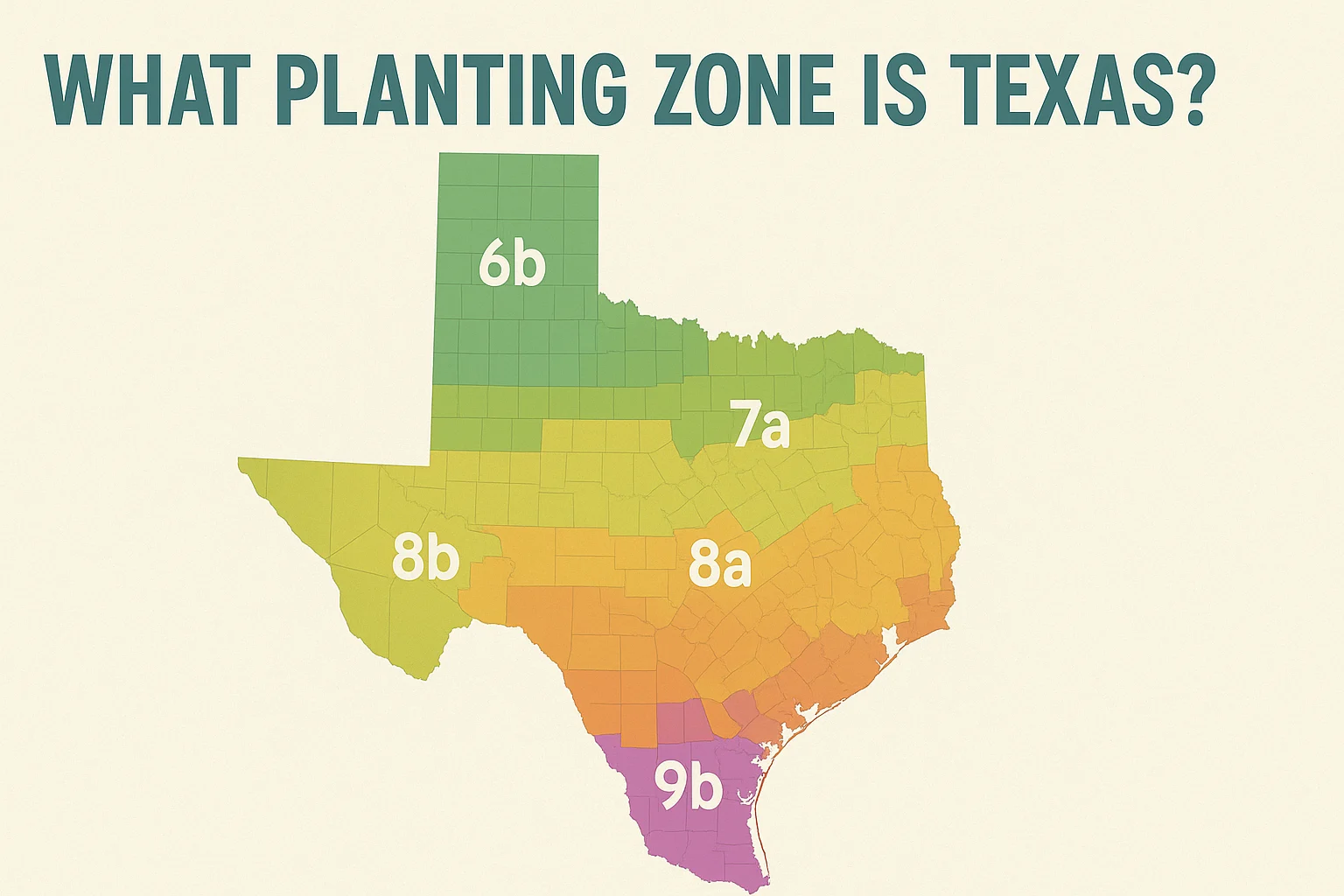
Texas’ planting zones range from 6a to 10a, with most of the state falling within zones 7b, 8a, and 8b. Northern Texas includes zones 6a, 6b, and 7a, while southern Texas is primarily in zones 9a, 9b, and even 10a along the Gulf Coast.
Whether you’re growing vegetables, flowers, or fruit trees, understanding what planting zone is Texas helps you choose plants that thrive in your specific area. With such a large and diverse state, Texas gardening conditions vary dramatically from Amarillo to Brownsville.
In this guide, we’ll cover the planting zones in Texas, break them down by region and city, and give you practical tips for successful gardening in every zone.
🗺️ What Planting Zone is Texas?
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zones in Texas span from Zone 6a in the north to Zone 10a in the south. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
| Region | USDA Planting Zone |
|---|---|
| Panhandle (Amarillo, Dalhart) | Zone 6a–6b |
| North Texas (Dallas, Fort Worth) | Zone 7a–8a |
| Central Texas (Austin, Waco) | Zone 8b |
| East Texas (Tyler, Longview) | Zone 8a–8b |
| West Texas (El Paso, Midland) | Zone 7b–8a |
| South Texas (San Antonio, Corpus Christi) | Zone 9a–9b |
| Gulf Coast (Houston, Brownsville) | Zone 9b–10a |
This wide range means gardeners in Texas must tailor their plant choices and growing schedules to their local planting zone.
📍 Texas Planting Zones by Major Cities
For a clearer view of what planting zone is Texas in your area, here’s how key cities fall:
| City | Planting Zone |
|---|---|
| Amarillo | Zone 6b |
| Lubbock | Zone 7a |
| Dallas | Zone 8a |
| Fort Worth | Zone 8a |
| Austin | Zone 8b |
| Houston | Zone 9a |
| San Antonio | Zone 9a |
| El Paso | Zone 8a |
| Corpus Christi | Zone 9b |
| Brownsville | Zone 10a |
If you’re wondering what planting zone is Texas in my city, this table gives a reliable reference point.
🌡️ Why Planting Zones Matter in Texas?
Knowing what planting zone is Texas where you live helps you:
- Select plants that can handle your local winter lows
- Time your planting and harvesting schedules
- Protect sensitive plants from frost
- Choose the right varieties for your microclimate
Texas’ size means there’s a stark contrast between the short growing seasons of the Panhandle and the nearly year-round planting opportunities near the Gulf Coast.
🌱 Gardening Examples: Zone 6b vs. Zone 9b in Texas
If you’re in Zone 6b (Amarillo), your first frost might hit by late October, cutting your warm-weather growing season short. Conversely, in Zone 9b (Corpus Christi), you might garden year-round, growing citrus, bananas, or even tropical ornamentals.
This diversity in planting zones in Texas requires localized knowledge and careful plant selection.
📅 Texas Planting Calendar by Zone
| Crop Type | Zone 6a-6b Start | Zone 8a-8b Start | Zone 9a-10a Start |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cool-season crops | Feb–Mar | Jan–Feb | Dec–Jan |
| Warm-season crops | Apr–May | Mar–Apr | Feb–Mar |
| Perennials | Fall or spring | Fall or spring | Fall preferred |
Your exact planting dates will vary, but knowing what planting zone is Texas in your region helps set realistic timelines.
🌵 Gardening Tips for Texas Climate Zones
Texas gardeners face unique challenges based on zone:
✅ Do:
- Mulch heavily to conserve water in hot, dry zones.
- Grow heat-tolerant varieties adapted to Texas summers.
- Watch for humidity-related diseases in Gulf regions.
- Amend soil based on region — sandy in West, clay-heavy in East.
❌ Avoid:
- Planting frost-sensitive plants too early in Zones 6a–7a.
- Ignoring drought risks in Zones 7b–8a.
- Forgetting about pests like grasshoppers and aphids.
Understanding what planting zone is Texas in your area informs these best practices.
Still Unsure About Your Zone?
To get an exact zone for your zip code, check the official USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Just enter your zip and you’ll see a color-coded zone that’s accurate down to your neighborhood.
Knowing what planting zone is Connecticut is the first step in planning a garden that lasts.
🧮 Recommended Tools for Texas Gardeners
Before you plant, use these calculators to plan efficiently:
- Soil Volume Calculator – Know exactly how much soil you need for raised beds.
- Plant Spacing Calculator – Prevent overcrowding and maximize yield.
- Indoor Plant Watering Calculator – Perfect for your houseplants or container garden.
❓ FAQs About Texas Planting Zones
What planting zone is North Texas?
North Texas falls mainly in Zone 7b to 8a, with cities like Dallas and Fort Worth in Zone 8a.
Can you grow citrus trees in Texas?
Yes, especially in Zones 9a, 9b, and 10a along the Gulf Coast. In colder zones, citrus must be grown in containers and brought indoors during winter.
When is the last frost in Texas?
- Zone 6b: Late April
- Zone 8a–8b: Late March
- Zone 9a–10a: Early March or earlier
✅ Conclusion: Know Your Planting Zone Before You Grow
Understanding what planting zone is Texas is essential for gardeners across this diverse state. From cold-hardy growers in Amarillo to subtropical enthusiasts near Brownsville, knowing your zone helps you grow smarter, avoid costly mistakes, and enjoy a thriving garden year after year.
