What Planting Zone is Georgia?[Map, Cities, and Growing Tips]
If you’re planning a garden or landscaping project in Georgia, one essential question needs answering: What planting zone is Georgia? Knowing your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone ensures you select plants that will thrive in your specific region. From the Blue Ridge Mountains to the coastal plains, Georgia’s diverse geography means its planting zones vary more than you might think.
In this guide, we’ll explain what planting zone Georgia is, how it affects your plant choices, and share essential growing tips tailored to the Peach State.
🌿 What Planting Zone is Georgia?
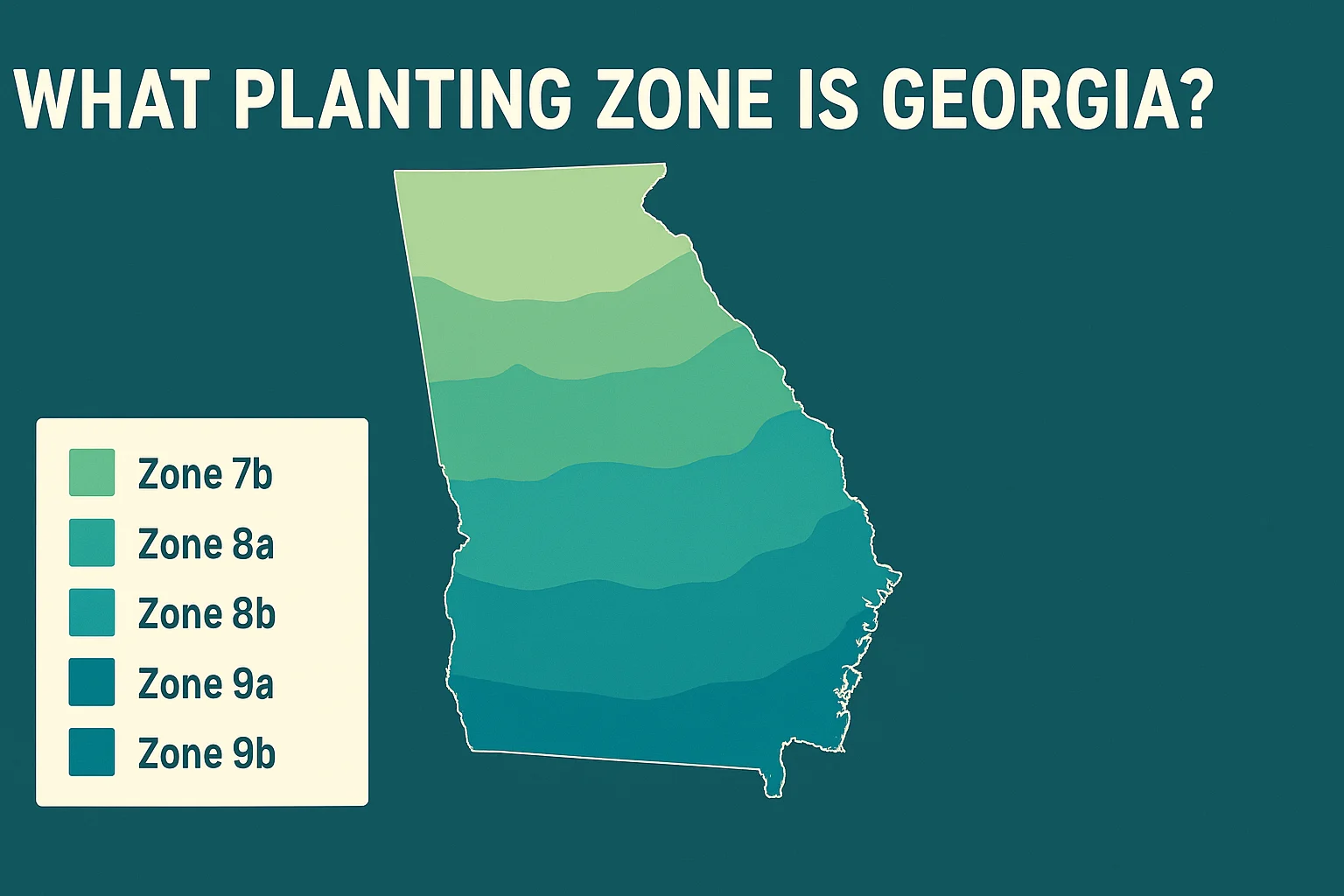
Georgia spans USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 7a through 9a, depending on your location within the state. This range is determined by the average minimum winter temperatures, which influence what perennials, trees, and shrubs can survive.
| Region | USDA Zone |
|---|---|
| Northern Georgia (e.g., Dahlonega, Blue Ridge) | Zone 7a |
| Central Georgia (e.g., Atlanta, Macon) | Zone 8a |
| Southern Georgia (e.g., Savannah, Valdosta) | Zone 9a |
So, what planting zone is Georgia? For most residents, it’s likely Zone 8a, but northern areas experience colder winters (Zone 7a), while the southern coastal region enjoys milder conditions (Zone 9a).
🗺️ Georgia Planting Zones by Major Cities
Here’s a breakdown of Georgia’s planting zones for key cities:
| City | Planting Zone |
|---|---|
| Atlanta | Zone 8a |
| Savannah | Zone 9a |
| Augusta | Zone 8a |
| Macon | Zone 8a |
| Columbus | Zone 8a |
| Athens | Zone 8a |
| Albany | Zone 8b |
| Valdosta | Zone 9a |
| Rome | Zone 7b |
| Blue Ridge | Zone 7a |
Again, the question of what planting zone is Georgia doesn’t have a single answer — it depends heavily on your exact location.
🌱 Why Knowing Georgia’s Planting Zone Matters?
Understanding what planting zone Georgia is helps you:
- Select plants that will survive year-round
- Time your planting schedules for vegetables and flowers
- Avoid frost damage to sensitive plants
- Plan for long-term growth of trees and shrubs
For instance, tropical plants might thrive in Savannah (Zone 9a) but struggle in Rome (Zone 7b). Conversely, cold-hardy plants may prefer the northern part of the state.
🍑 Example: Tomato Planting in Georgia’s Zones
In Zone 7a (like Blue Ridge), tomato planting usually begins in late April after the last frost. However, in Zone 9a (like Savannah), you can start planting as early as March. The difference in planting zones affects not just timing, but also harvest yields, pest pressures, and growing season length.
The answer to what planting zone is Georgia directly determines how you approach your garden plan.
🗓️ Planting Calendar for Georgia by Zone
| Crop Type | Zone 7a Start | Zone 8a Start | Zone 9a Start |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cool-season crops (lettuce, kale) | Feb–Mar | Jan–Feb | Dec–Jan |
| Warm-season crops (tomatoes, peppers) | Apr–May | Mar–Apr | Feb–Mar |
| Perennials | Fall/Early Spring | Fall/Early Spring | Fall (best) |
Being aware of what planting zone is Georgia helps you plant with confidence and avoid common mistakes like planting too early or too late.
🌤️ Georgia’s Climate & Gardening Tips
Georgia has a humid subtropical climate, which means hot, humid summers and mild winters — but it varies significantly by zone.
✅ Do:
- Use mulch to combat weeds and retain moisture
- Choose heat-tolerant and disease-resistant varieties
- Improve clay-heavy or sandy soils with compost
- Watch for pests like aphids, squash bugs, and hornworms
❌ Avoid:
- Overwatering, especially during rainy seasons
- Planting frost-sensitive crops too early in Zones 7a/7b
- Ignoring local microclimates (urban heat islands, valleys)
No matter where you are, knowing what planting zone is Georgia in your area helps prevent costly gardening mistakes.
🧮 Helpful Gardening Tools for Georgia Gardeners
Planning a garden in Georgia? These calculators will make your life easier:
- Soil Volume Calculator – Know exactly how much soil you need for raised beds.
- Plant Spacing Calculator – Prevent overcrowding and maximize yield.
- Indoor Plant Watering Calculator – Perfect for your houseplants or container garden.
These tools complement your understanding of what planting zone is Georgia, providing practical help for everyday gardening tasks.
🙋 FAQs About Georgia Planting Zones
What is the main planting zone for Georgia?
The majority of Georgia falls under USDA Zone 8a, which is ideal for a wide range of plants, from vegetables to perennials.
Can I grow citrus trees in Georgia?
Yes, but mainly in Zone 9a areas like Savannah or Valdosta. In colder zones, citrus should be grown in containers and moved indoors during winter.
When is the last frost in Georgia?
- Zone 7a: Mid-April
- Zone 8a: Late March
- Zone 9a: Early March or earlier
Knowing what planting zone is Georgia will help you estimate frost dates accurately.
✅ Conclusion: Why Planting Zones Matter for Georgia Gardeners
If you’re serious about gardening in Georgia, understanding what planting zone is Georgia is non-negotiable. Whether you’re planting delicate flowers, hearty vegetables, or shade-giving trees, your zone dictates what will thrive and what might fail.
Georgia’s planting zones (7a to 9a) give you a unique advantage — a long growing season with diverse planting options. Take the time to identify your zone, plan accordingly, and you’ll enjoy a lush, productive garden season after season.
