🌳 Tree Age Calculator
Use this calculator to estimate a tree’s age from its trunk measurements.
This calculator uses a rough rule of thumb:
Age ≈ Diameter (inches) × Growth Factor
If you only have the tree’s circumference, we calculate diameter as:
Diameter = Circumference / π
Measuring Tips:
- Measure at 4.5 ft above the ground (DBH).
- Use a tape for circumference or calipers for diameter.
Growth Factors by Species:
| Species | Growth Factor | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oak | 5 | Slow but steady growth |
| Maple | 4 | Moderate growth rate |
| Pine | 3 | Faster early growth |
| Redwood | 10 | Grows tall and fast |
| Other | 4 | Fallback estimate |
Tree Age Calculator – Estimate Tree Age by DBH

Created by James S. Lockwood
With a background in botany and ecological sciences, James specializes in creating practical tools and resources to help gardeners, farmers, and plant enthusiasts optimize their green spaces.
Our Tree Age Calculator helps you estimate the age of a tree using simple measurements like trunk circumference or diameter at breast height (DBH). Whether you’re a homeowner curious about an old oak in your yard or a forester needing a quick estimate, this tool gives you an easy, non-invasive way to calculate a tree’s approximate age—without cutting it down or counting rings. Just enter the tree’s species and size, and get an instant estimate based on average growth rates.
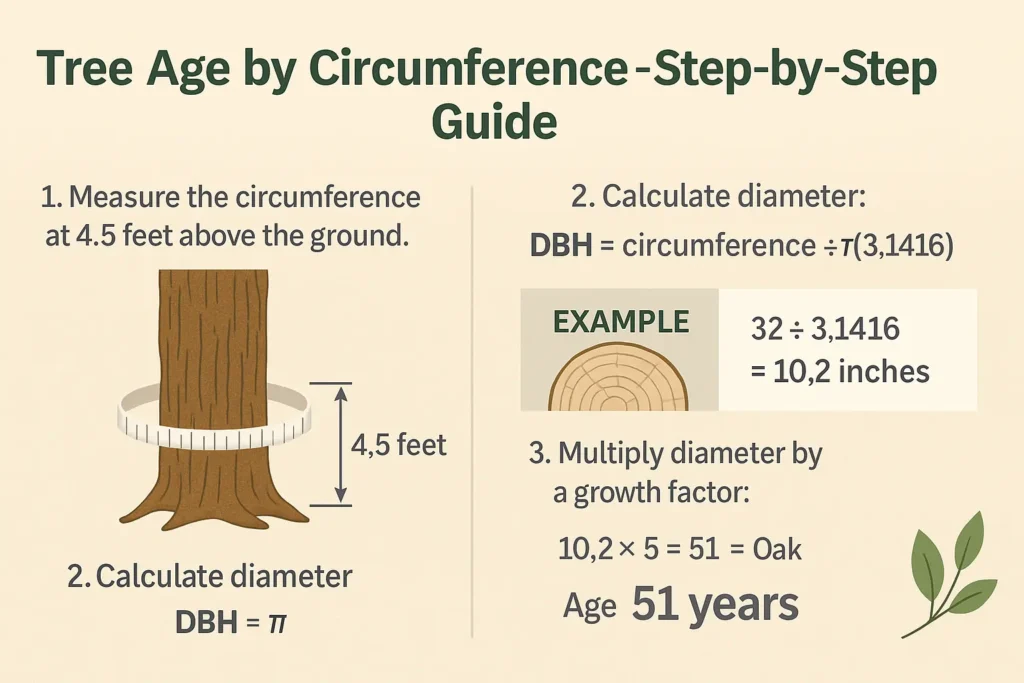
Table of Contents
How Tree Age Is Typically Calculated?
The most widely accepted method for estimating tree age (without cutting it down) involves measuring the trunk’s diameter at breast height (DBH) and multiplying it by a species-specific growth factor. It sounds simple—and for the most part, it is.
Here’s how the process works:
- Measure Circumference: Wrap a measuring tape around the tree trunk at 4.5 feet from the ground. That’s the standard “breast height” used in forestry.
- Calculate Diameter: Divide that circumference by π (3.14). The result is your DBH. If you’d like help with this step, try our Tree Diameter Calculator for an instant conversion.
- Multiply by Growth Factor: Each tree species grows at a different rate. An oak’s growth factor might be 5, while a pine could be around 3. Multiply DBH by this factor.
Example:
A red maple with a trunk circumference of 75 inches has a DBH of roughly 23.9 inches. Multiply that by its growth factor (4.5), and you get an estimated age of about 108 years.
Of course, this assumes ideal growing conditions—which rarely exist in real life. A tree growing in a crowded forest might grow more slowly than the same species in an open park. Some trees are even stunted by poor soil or urban pollution, aging more “mentally” than physically, if you will.
If you’d rather skip the math, use our Tree Age Calculator to instantly estimate the age based on diameter and species: Tree Age Calculator you can add link to tree diameter and basal area calc
Estimating Tree Age by Species
Growth rates vary wildly across tree species. Here’s a quick look at the typical growth factors used in calculations:
Growth Factors by Tree Species
Different tree species grow at different rates. Below are approximate growth factors for common species:
| Tree Species | Growth Factor | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oak | 5 | Slow but steady growth |
| Maple | 4 | Moderate growth rate |
| Pine | 3 | Conifers often grow faster early |
| Birch | 3 | Grows quickly but shorter lifespan |
| Elm | 4 | Adapts to urban environments |
| Palm | 2 | Slow-growing species |
| Spruce | 3 | Common in colder climates |
| Fir | 3 | Similar growth to spruce |
| Cypress | 4 | Can grow tall in wet areas |
| Willow | 4 | Fast-growing species |
| Redwood | 10 | Can grow very large, very quickly |
| Fruit Trees | 3 | Growth varies by fruit type |
| Other/Unknown | 4 | General fallback estimate |
These are only averages. A healthy, well-watered oak might outpace a struggling fir. This is why using multiple tools in combination—such as a DBH Basal Area Calculator or even a Tree Diameter Calculator—can give you a more complete understanding.
If you’re curious about timber value, you can also check the Cedar Tree Value Calculator or Oak Tree Value Calculator. Older trees, unsurprisingly, are often more valuable.
Using Tree Rings to Determine Age

To estimate a tree’s age using its rings, you typically count the number of annual rings visible in a cross-section of its trunk. Each ring generally represents one year of growth, but there can be variations depending on factors like species, location, weather, and overall health.
Tree rings form because trees grow at different rates during the year—faster in the spring and slower in late summer or fall. This difference creates a contrast in the wood’s color and density, forming a visible ring. In temperate climates, where seasons are distinct, ring formation is consistent and reliable.
How to Count Tree Rings:
If the tree has been cut down, examine the flat stump or log end.
Start at the center (the pith) and count outward—each ring moving toward the bark represents one year.
For living trees, professionals use a tool called an increment borer to extract a thin core sample, allowing the rings to be counted without damaging the tree.
Important Notes:
False Rings: Some trees, especially under stress (like sudden drought or insect damage), may form more than one ring in a single year.
Missing Rings: In extreme conditions, a tree might grow very little, causing a ring to be barely visible or missing altogether.
Hard to Read: Tropical trees or trees in uniform climates may not form clear rings, making this method less reliable.
Decay: Older trees often have rot or hollow centers, which can erase the earliest rings and obscure true age.
Despite these limitations, counting tree rings—known as dendrochronology—is the most accurate way to determine a tree’s age when the core or stump is available. It’s widely used in forestry, ecology, and even archaeology to study climate patterns and environmental changes over centuries.
For those who don’t have access to a cut trunk or an increment borer, using a Tree Age Calculator based on trunk diameter and species offers a practical and non-invasive alternative.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I tell a tree’s age without cutting it down?
Use a tape measure to get its circumference at breast height, divide by 3.14 to get diameter, and multiply by the species growth factor. Or use a tree age calculator for quick results.
Can I tell tree age from diameter alone?
Only if you also know the species and apply the correct growth factor. A 15-inch DBH could mean 30 years for a fast-growing tree or 75 years for a slow-growing one.
What’s the oldest tree on Earth?
The oldest known tree is Methuselah, a Great Basin bristlecone pine in California, believed to be over 4,800 years old.
Does bigger always mean older?
Not always. Some trees grow quickly in ideal environments. Others, like bonsais, remain tiny but could be decades old. Check both tree size and species for a more accurate estimate.
How do I estimate age if I only have a photo?
There are emerging tools like tree age calculator apps and AI-driven estimators. Some even claim to estimate tree age by analyzing photo metadata and visible characteristics. While not always reliable, they can provide ballpark figures.
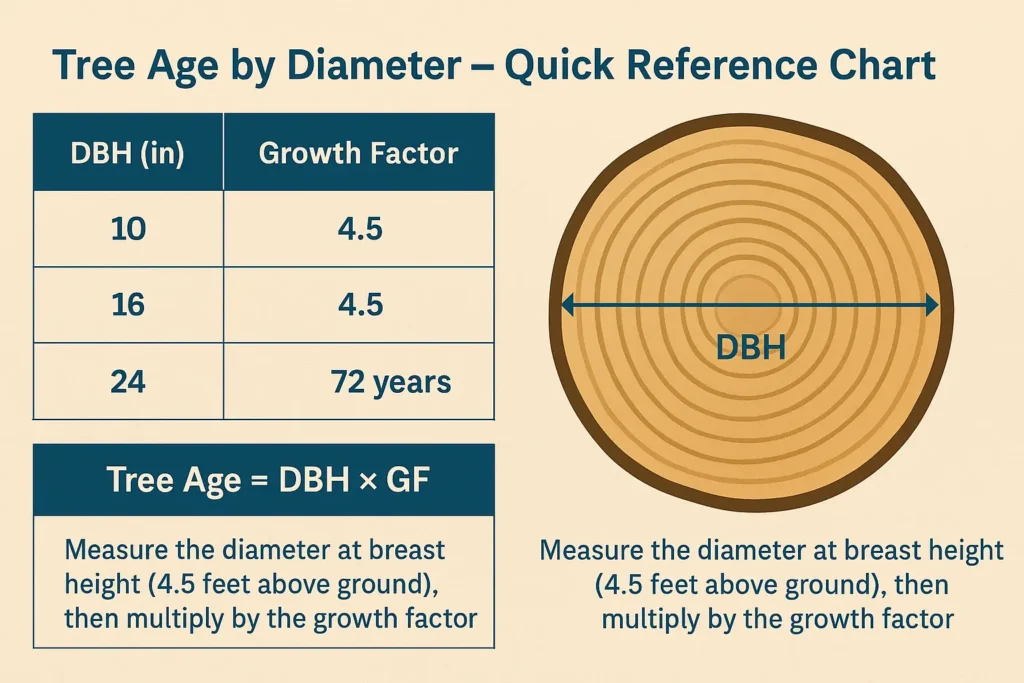
Tree Age Chart: Quick Reference
Note: These numbers assume healthy trees growing in open spaces.
If you’re working with urban trees or forests, it’s wise to compare age estimates with tools like the Tree Height Calculator, Tree Leaves Calculator, or even a Tree Value Calculator. Together, these tools help paint a broader picture of a tree’s condition, not just its age.
Other Ways to Gauge Tree Age
By Species Chart: A Tree Age by Diameter Chart helps visualize rough ages across species.
Apps and Tools: Use a Tree Age Calculator App or online platforms.
Rings or Core Sampling: If permitted and you have arborist tools, this is the gold standard.
Visual Indicators: Deep bark fissures, moss presence, and trunk thickness often hint at age but are subjective.
For professionals and enthusiasts alike, this tree growth factor chart from TreesCharlotte is a helpful external reference.
Final Thoughts
Tree age isn’t always obvious—and it’s rarely exact. Two oaks, planted a year apart, might differ by 20 years in appearance depending on their location and care. That’s why using a tree age calculator is a great start, but not the end of your journey.
Mix in tools like the DBH Calculator, Tree Height Calculator, or even Tree Value Estimator to get a more nuanced view. And always consider the context: species, soil, sunlight, and stressors. Tree aging is as much an art as a science.
Sometimes the tree’s story is more important than its age.
Disclaimer for Tree Age Calculator
This tool provides estimated tree ages based on standard growth rates. Actual tree age may vary due to soil conditions, climate, and species variation. For official age verification, consult a certified arborist.
Discover Tree & Forestry Calculators
